A102
Difference between revisions of "A102"
m (1 revision imported) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 03:26, 5 October 2017
The activities associated with identifying and defining existing physical supply chains of a business. A physical supply chain is a unique geography/supplier/product/market/customer combination for the fulfillment of customer orders. The purpose of supply chain discovery is to identify all existing material or service flows within a business and serve as the input to the supply chain segmentation process.
Contents
Use Cases
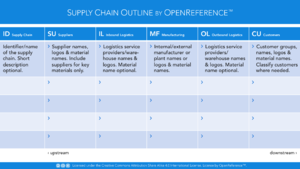
Supply Chain Outline: A template for summarizing end-to-end, upstream and/or downstream supply chains. The outline recognizes the following supply chain level roles (functions/partners):- Suppliers (SU) - The internal or external partners that provide key materials for this supply chain. This list is typically limited to the key materials, suppliers or supplier classes.
- Inbound Logistics (IL) - The freight forwarders, carriers, internal functions or external partners that provide transport and other logistics services (e.g. export, import) for this supply chain. This list is typically limited to the primary service providers.
- Warehouses (WH) - The Warehouse facilities, yards, internal functions or external partners that provide warehousing and other services (e.g. kitting, breaking bulk) for this supply chain.
- Manufacturing (MF) - The plants, internal functions or external partners that provide manufacturing, repair, remanufacturing, recycling activities for this supply chain.
- Distribution Centers (DC) - The DCs, warehouse facilities, internal functions or external partners that provide distribution center and other services (e.g. repacking, consolidation, de-consolidation, warehousing) for this supply chain.
- Outbound Logistics (OL) - The freight forwarders, carriers, internal functions or external partners that provide transport and other logistics services (e.g. export, import) for this supply chain. This list is typically limited to the primary service providers.
- Installers (IS) - The internal functions or external partners (e.g. installers, distributors) that provide on-site installation, assembly activities for customers for this supply chain.
- Channel Partners (CH) - The external partners that provide local presence, warehousing, delivery services in regions where this supply chain would have no presence.
- Customers (CU) - The internal functions or external customers (e.g. consumers, strategic partners) that acquire materials or services from this supply chain.
Consider the Channels, Customer Segments, Key Resources, Key Partners, and Key Activities from the Business Model Canvas when completing the template.
Notes
The sum of the revenue of the Demand Segments listed should equal the total revenue of the business. The sum of the Cost of Goods Sold of the Supply Segments listed should equal the total COGS of the business.
Not every supply chain requires partners for each category. However, every supply chain typically requires suppliers and customers. Digital products or services do require outbound logistics, these partners provide web/data services instead of physical transport.
The columns in the template are populated to facilitate a basic manufacturing supply chain. More complex supply chains may require more columns and/or repeating columns.
Workflow
| Process |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A102 |
|
||||||||||||